11/29/2017
11 Useful split command examples for Linux/UNIX systems
https://www.linuxtechi.com/split-command-examples-for-linux-unix/
11/13/2017
20 Sed (Stream Editor) Command Examples for Linux Users
https://www.linuxtechi.com/20-sed-command-examples-linux-users/
11/07/2017
How to get octal file permissions on Linux/Unix command line
https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/get-octal-file-permissions-from-command-line-on-linuxunix/
11/02/2017
Three Alternatives for Enabling Two Factor Authentication For SSH On Ubuntu 16.04 And Debian Jessie
https://bash-prompt.net/guides/ssh-2fa/
Labels:
BookMark,
Linux,
SSH,
Two Factor Authentication
10 Best Lightweight Linux Distributions For Older Computers In 2017
https://itsfoss.com/lightweight-linux-beginners/
Important Docker commands for Beginners
http://linuxtechlab.com/important-docker-commands-beginners/
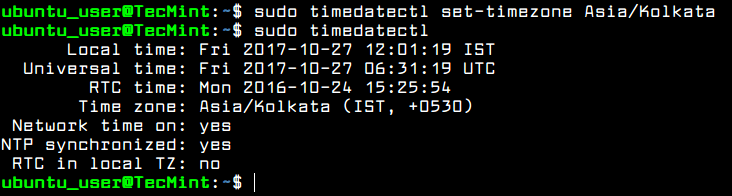
Set Ubuntu Server Time
To control or query Ubuntu server clock and other related time settings, execute timedatectl command with no argument.
In order to change your server’s time zone settings, first execute timedatectl command with list-timezones argument to list all available time zones and, then, set the time zone of your system as shown in the below excerpt.
$ sudo timedatectl $ sudo timedatectl list-timezones $ sudo timedatectl set-timezone Europe/Vienna
The new systemd-timesyncd systemd daemon client can be utilized in Ubuntu in order to provide an accurate time for your server across network and synchronize time with an upper time peer server.
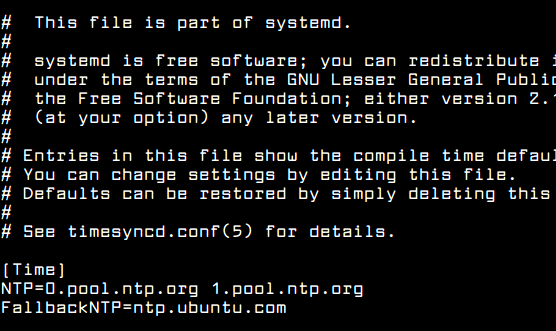
To apply this new feature of Systemd, modify systemd-timesyncd daemon configuration file and add the closest geographically NTP servers to NTP statement line, as shown in the below file excerpt:
$ sudo nano /etc/systemd/timesyncd.conf
Add following configuration to timesyncd.conf file:
[Time] NTP=0.pool.ntp.org 1.pool.ntp.org FallbackNTP=ntp.ubuntu.com
To add your nearest geographically NTP servers, consult the NTP pool project server list at the following address: http://www.pool.ntp.org/en/
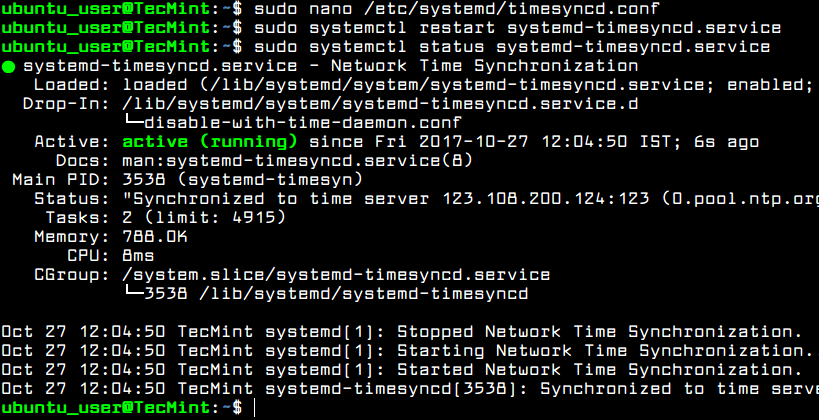
Afterwards, restart the Systemd timesync daemon to reflect changes and check daemon status by running the below commands. After restart, the daemon will start to sync time with the new ntp server peer.
$ sudo systemctl restart systemd-timesyncd.service $ sudo systemctl status systemd-timesyncd.service
credit by https://www.tecmint.com/initial-ubuntu-server-setup-guide/
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)